Book an Appointment
Call Us+91 9319488481A traumatic brain injury (TBI) occurs when an external force, such as a blow, jolt, or penetration, damages the brain. This injury occurs when the head or body is struck or shaken hard enough to disrupt normal brain function. It is so mild, moderate, or severe in impact and can lead to complications that last for life, hence diagnosis and treatment as soon as possible from the injuries depict better recovery chances.
TBIs can result from car accidents, falls from heights, or high-contact sports like football or hockey. Depending on severity, the effects can be short-term, like a mild concussion, or more serious, causing lasting physical, cognitive, or psychological changes.
There are several types of TBIs, each bringing on unique challenges: 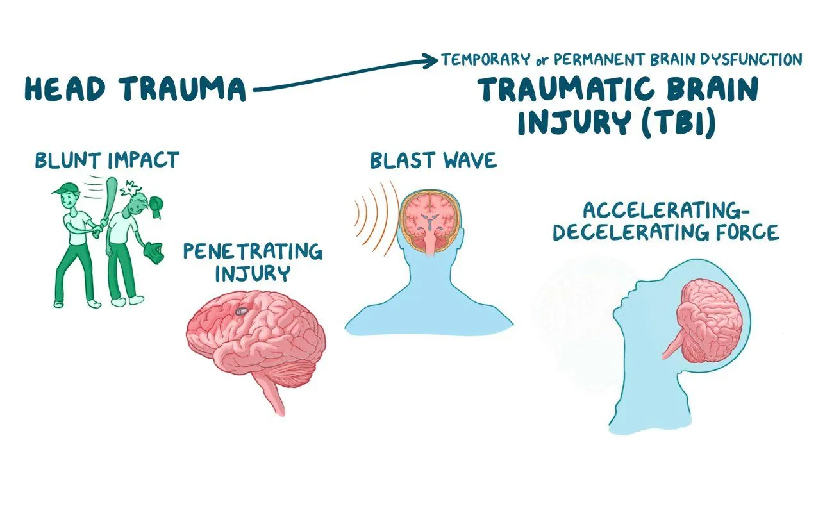
Concussion: Most common and mildest form of TBI, which usually results from a blow to the head. Such injuries will cause a brief unconsciousness or confusion but seldom cause persistent damage if treated. Contusion: This is bruising on the brain tissue due to a direct impact. Contusions are usually worse than concussions and may require treatment.
Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI): DAI is a more severe form of TBI that is caused when the brain moves inside its skull, breaking many nerve fibers. Typically associated with high-speed automobile accidents or violent shaking, DAI can bring very poor long-term consequences.
Other forms of TBI include penetrating injuries, some objects piercing the skull-or hematomas, when the bleeding occurs within or around the brain.
TBIs can occur in various situations, and knowing the causes helps with prevention.
Motor Vehicle Accidents: Automobile, motorcycle, and bicycle crashes are also common causes of TBIs. The severity and nature of the impact frequently cause extensive damage to the brain.
Sports Injuries: Contact sports like football, hockey, rugby, and even soccer can lead to TBIs if proper safety gear is not used.
Falls: Among the leading causes of TBIs are falls from heights due to slipping, tripping, and falling among children and the elderly.
Acts of Violence: These involve assaults, domestic violence, and gunshot wounds, which may result in penetrating brain injuries or blunt trauma leading to TBIs.
The symptoms of a Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) vary extensively with the type and severity of the injury. In slight cases, the symptoms can be relatively mild and temporary, whereas in severe TBIs, symptoms are usually long-lasting or even permanent. These often include symptoms such as:
Any of these symptoms occur after a head injury prompts an urgent visit to the emergency room.
Doctors diagnose a TBI using a combination of patient symptoms and clinical assessment. Simplify for clarity:
"However, diagnosing a mild TBI (mTBI) can be less clear-cut, often relying more on assessing the individual's symptoms.
Proper diagnosis is essential to the assessment of the level of severity of a TBI and the designing of the most appropriate treatment program. Usually, diagnosis is conducted through the following stages:
Determine medical care immediately after the head injury. Emergency workers or physicians will do an initial evaluation assessing consciousness, motor activity, and the degree of the injury.
Your doctor will discuss your medical history and the events that occurred preceding the injury. A physical examination to assess your general medical condition, including for example visible signs of trauma like bruising, and basic neurological functions such as reflexes and coordination, will be conducted.
Doctors often use CT scans and MRIs to determine the severity of the brain injury. In these scans, detailed images of the brain are shown which enable the detection of structural damage, bleeding, or swelling.
The healthcare provider may request that the patient undergo several tests to assess his cognitive skills, for example, his memory, problem-solving, and coordination. Such tests help establish the extent to which the injury affects the functionality of the brain and the level of impairment that is expected to be incurred.
In some instances, a blood test may be prescribed to evaluate another condition that might mimic the symptoms of TBI. Such conditions include infection or metabolic imbalance.
Treatment of TBI is based on its severity. Mild TBIs, such as concussions, would normally just need rest and proper monitoring while the most severe cases require more intense care and rehabilitation.
Rest and Observation: In minor TBIs, doctors may recommend rest in body and mind. They have to observe to know if the symptoms of TBIs progress because sometimes symptoms of TBIs worsen with time.
Surgery:In severe cases, surgery may be required to treat brain bleeding or swelling and can relieve pressure in the brain by removing clots.
Medications are given either to manage symptoms or avoid complications. Medications help control many symptoms. Here are some examples:
Pain Relievers: These are given in the form of drugs to alleviate headaches and other pains.
Anticonvulsants: To prevent the induction of seizures in extreme cases of severe TBI.
Diuretics: To remove the swelling that is present in the brain.
Coma-inducing Drugs: In extreme conditions of swelling, medically induced coma will reduce activity and pressure inside the brain.
Rehabilitation is often a part of the treatment protocol, especially for those with a TBI of moderate to severe intensity. Patients may necessitate various types of therapies depending on the nature of the impairment in their condition:
Physical Therapy: Strengthening muscles, balance, and coordination
Occupational Therapy: Restoring the ability to perform simple everyday activities, such as dressing and eating at home or work, is a focus of treatment.
Speech Therapy: Restoring lost communication skills due to TBI
Psychotherapy: Emotional healing support in depression, anxiety, or even through a behavioral change following TBI
Generally, TBI recovery requires long-term care. Regular follow-ups help healthcare professionals monitor progress and address any complications that may arise. Treatment often requires constant adjustments to meet the patient’s evolving needs.
Major rehabilitation can take various cognitive, emotional, and physical features for months or years after an injury in some cases.
Although Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBI) may be somewhat long-lasting, they should be diagnosed and treated as early as possible to enable patients to recover soon. Both minor concussions and severe brain injuries require immediate consultation with a doctor. In Bangalore, numerous expert doctors and leading institutes offer the best treatment options to support recovery.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of TBI, do not wait. Take proper steps to preserve your brain health and enhance your chances to recover completely.
Are you or someone you know struggling to recover from a traumatic brain injury (TBI) treatment in Bangalore? Walk Again Rehab offers comprehensive and personalized treatment plans in Bangalore to help you regain your independence and quality of life.