Book an Appointment
Call Us+91 9319488481A stroke can be life-altering, leaving lasting physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges. Yet, it is not the end of the road. Thanks to advancements in neurorehabilitation, stroke survivors have the potential to regain their independence and improve their quality of life.
Neurorehabilitation involves an array of treatments that aid in regaining lost functions, promoting mobility, and facilitating recovery. This extensive process capitalizes on the ability of the brain to rewire itself (referred to as neuroplasticity) to overcome the injury caused by the stroke. Through the right strategy, including physical therapy, speech therapy, and advanced treatments like brain stimulation, recovery from a stroke is not just possible—it is achievable.
 Neurorehabilitation is a special form of treatment that may assist an individual with a neurological condition, e.g., a stroke. After a stroke, the brain can be highly damaged, but through proper treatment, the brain can "rewire" itself through neuroplasticity. What this means is that the other areas of the brain can take over the function of the areas of the brain that are destroyed.
Neurorehabilitation is a special form of treatment that may assist an individual with a neurological condition, e.g., a stroke. After a stroke, the brain can be highly damaged, but through proper treatment, the brain can "rewire" itself through neuroplasticity. What this means is that the other areas of the brain can take over the function of the areas of the brain that are destroyed.
The aim of neurorehabilitation is to maximize recovery by employing therapies that target mobility, cognitive function, and emotional health. The combination of physical, occupational, and speech therapy is typically complemented by newer techniques like brain stimulation to achieve the maximum results.
Read Also: What is Advanced Neuro Rehab?
Central to neurorehabilitation is the premise of neuroplasticity—namely, the brain's amazing ability to reorganize and form new connections following injury like a stroke. When one stroke damages an area of the brain, areas of the healthy brain can catch up by adopting the lost activities. The trick to unlocking such potential is rehabilitative exercises and therapies that challenge brain activity and stimulate the forming of new paths.
Early and consistent therapy is necessary because the brain's reorganization capacity is greatest in the first few months after a stroke. The greater the brain's engagement in rehabilitation, the more function lost like walking, talking, and memory will come back.
Read Also: Choosing the Best Neuro Rehab Center for You: Factors to Consider
A rehabilitation program for a stroke that is effective involves various therapies, each of which is intended to regain a particular function. Let us consider the most important therapies involved in neurorehabilitation in greater detail.
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of stroke rehabilitation. Movement may be restricted for many stroke survivors, and walking or even simple motor activities may prove challenging. Physical therapy seeks to restore strength, balance, and coordination. The exercises are modified to suit individual patients, from enhancing muscle strength to enhancing joint mobility.
The goal is to regain movement function, whether walking again or performing simple activities like bending or standing. Physical therapists also attempt to prevent complications such as muscle spasticity and joint deformity, which can occur after a stroke.
While physical therapy focuses on gross motor skills, occupational therapy is focused on fine motor skills and activities of daily living (ADLs). Dressing, eating, or bathing are some activities that survivors of stroke can struggle with. Occupational therapists help clients learn to adapt to these challenges and restore their independence.
Assistive equipment like grab bars or assistive utensils can be brought in periodically to aid activities of daily living. The patient is also aided by the therapist to improve fine motor skills, i.e., writing or buttoning. The patient's ability to perform simple activities is enhanced.
In case of patients who have a speech or language part of the brain involved in stroke, speech and language therapy becomes a requirement. Disorders such as aphasia, where individuals become unable to communicate, are relatively common after stroke. Speech therapists assist patients to restore the use of speech, understand language, and read and write once more.
Also, if a stroke damages swallowing (dysphagia), speech therapists provide methods of safely eating and drinking, preventing choking or aspiration pneumonia.
Emerging therapies like transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and deep brain stimulation (DBS) are being more and more utilized in stroke rehabilitation. These therapies consist of electrical pulses to stimulate specific areas of the brain, enhancing recovery and inducing neuroplasticity.
By electrically exciting regions of the brain that have been damaged, brain stimulation can restore motor function, speech, and cognitive abilities. While these treatments are in their early stages, initial research suggests they have a significant potential to improve stroke recovery, particularly in cases where conventional therapies are inadequate.
Robotic-assisted therapy utilizes the application of highly advanced robotics in order to aid and guide the repetitive movement of stroke survivors. The robotic mechanisms ensure precision and consistency, with the added ability to give instant feedback to ensure correct exercise completion. The repetitiveness in the exercises enables the recovery of motor functions such as walking or hand movement.
Robotic therapy also allows for longer rehabilitation therapy, as the patient is able to exercise for extended periods of time without fatigue. This complementarity of precision and extended therapy sessions can lead to exceptional results.
Read Also: Rehabilitation Centres In Delhi And India: Everything You Need To Know
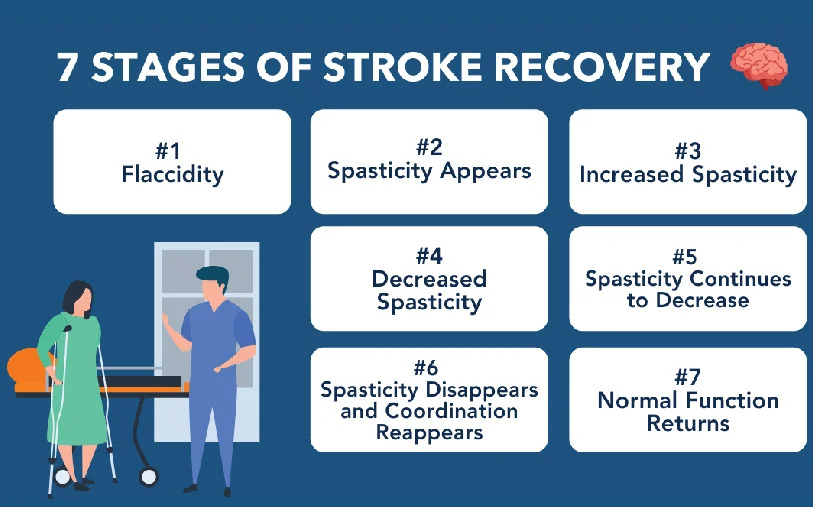
Recovery from stroke is a process that is undertaken in several stages. Every stage has different challenges and milestones, and rehabilitation must be dynamically modified accordingly. Here is a brief overview of the significant stages:
In the first few days or weeks following a stroke, the immediate focus is on stabilizing the patient’s condition. Medical teams monitor vital signs, manage any complications, and prevent further damage. During this time, rehabilitation may begin in the form of passive exercises, such as range-of-motion activities, to keep muscles from weakening or stiffening.
Once the patient stabilizes, rehabilitation is more intense. This process typically lasts from several weeks to months and involves more intense physical, occupational, and speech therapies. Stroke survivors start working on regaining basic mobility skills such as sitting, standing, and walking and re-establishing finer motor skills for activities like eating or writing.
The chronic phase can last months or years, with therapy continuing to refine motor skills and mental capacity. Improvement tapers off, but ongoing rehabilitation can still lead to physical, mental, and emotional improvement. Throughout this phase, neuroplasticity is still an integral part of healing.
Read Also: The Role Of Neurorehabilitation In Stroke Recovery
Early rehabilitation is critical to the success of stroke recovery. The brain's reorganization ability is greatest in the first few months after a stroke. Early intervention can initiate neuroplasticity, allowing stroke survivors to recover lost functions more quickly and improve overall outcomes.
Research has proven that the sooner the rehabilitation process is started, the greater the percentage of full recovery. Early intervention also reduces the risk of complications such as blood clots, muscle atrophy, and joint deformities, which can hinder progress.
Read Also: Optimizing Stroke Recovery: Tips and Effective Therapies
Neurorehabilitation sheds light of hope for patients suffering from strokes by enabling them to regain the lost strengths and become independent to a greater level in daily lives. It employs the advantages of neuroplasticity along with some interventions like physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and advanced methods in brain stimulation for stroke patients. For patients to improve to their maximum potential, restore lost potential, and enjoy increased independence, early intervention, combined team therapy, and after-care are of the utmost significance.
Stroke recovery is a slow and arduous process, but with the right therapy and will power, the road to healing is always a possibility.