Book an Appointment
Call Us+91 9319488481A stroke is one of the most life-changing events, as interruptions in the brain's arterial supply can lead to severe physical, cognitive, and emotional effects. Stroke recovery varies significantly between individuals, depending on factors like the severity of the stroke, location of brain damage, and the rehabilitation received. However, with timely medical intervention complemented by holistic rehabilitation, many stroke survivors can recover at least part or even the majority of their functions. We will look at life after a stroke, the kinds of strokes, their implications, treatment options, rehabilitation, and finally the recovery process in depth.
A stroke typically occurs suddenly and requires immediate medical attention to minimize damage. Strokes fall into two categories.
A blood clot blocking a blood vessel in the brain causes an ischemic stroke. This accounts for about 85% of all strokes. The blockage could be caused by the buildup of fatty deposits in blood vessels or blood clots coming from other parts of the body and traveling to the brain.
It happens when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures and starts to leak blood into or around the brain tissue. While not as prevalent, hemorrhagic strokes are generally more fatal. They result mostly from issues like hypertension, aneurysms, or arteriovenous malformations.
Knowing stroke onset warning signs enables one to treat the condition early. Common signs include:
The severity and duration of these symptoms can vary, but immediate medical attention is crucial in improving outcomes.
While a stroke can cause permanent damage, timely medical care and rehabilitation can enable many people to recover significant functions.No treatment can be done to restore lost function. While some lost functions may not be fully restored, survival and long-term recovery are possible with immediate treatment, though outcomes depend on the stroke’s severity and the patient’s health.
The extent and nature of brain damage determine the effects that a stroke has. The consequences that may result from a stroke include the following:
Physical impairments: Weakness, paralysis, or inability to walk. Poststroke survivors experience hemiplegia, which is the weakness of one body side, or hemiparesis most often.
Cognitive challenges: Memory loss, inability to focus, or judgment.
Emotional disorders: Depression anxiety and mood swings are prevalent because stroke survivors have to deal with loss of capabilities and reliance on others.
Living with the aftermath of a stroke can be a challenging experience, but it can also serve as a lesson in strength and resilience. Stroke survivors face physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges but, with the right support, many regain their independence.
Problem Walking: The paralysis of one half of the body creates the trouble of walking and doing daily work. A lot of people are compelled to use canes, walkers, or wheelchairs.
Fatigue: Fatigue is common after a stroke and can sometimes hinder rehabilitation. Energy conservation strategies and rest periods must be established.
Memory and Attention Deficits: Most stroke patients experience problems of memory loss and attention deficits that create challenges while performing simple tasks.
Problem-solving Difficulties: Problems in decision-making and complex work may become impossible to handle; therefore, a critical need exists to formulate new strategies to cope with the situation.
Depression and Anxiety: Emotionally, the impact of a stroke can be quite powerful. Many patients enter into a state of loss, frustration, or fear concerning their future.
Social Isolation: Impairments in physical and cognitive functions may influence the lowered level of social interactions.
However, many stroke patients are known to retain significant reservoirs of strength.With support from doctors, caregivers, and loved ones, many stroke survivors can regain independence, achieve their goals, and find renewed purpose.
Urgent medical care is highly essential when a stroke occurs. With an ischemic stroke, restoring blood flow to the brain should be done as quickly as possible.This is primarily achieved by:
Thrombolytics: An enzyme named tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) is given to dissolve the clot if admitted within several hours of the start of the symptoms
Mechanical thrombectomy: Use of catheter for mechanical removal of clot from the blocked blood vessel.
For hemorrhagic strokes, treatments focus on controlling bleeding and reducing brain pressure.
Surgery: For more severe conditions, surgery will be necessary, where the damaged blood vessel will have to be repaired and pressure in the brain relieved.
Medications: Medications to lower blood pressure or prevent seizures also would be essential.
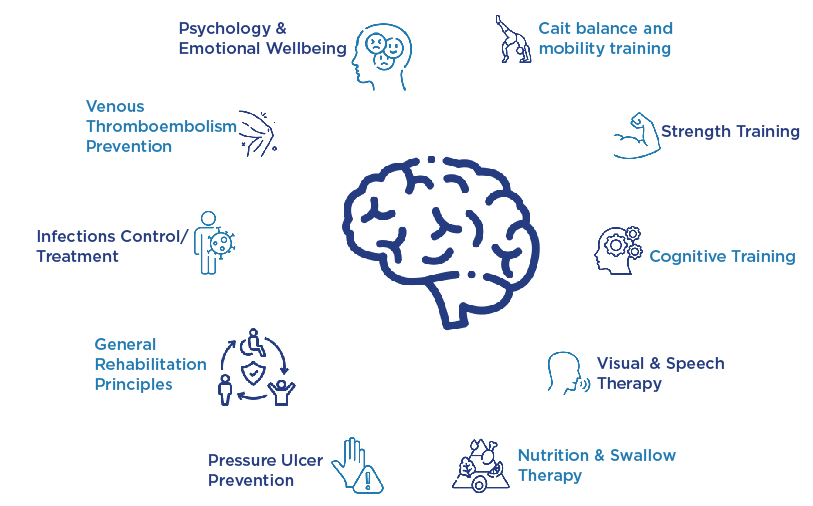
Rehabilitation is an individualized, long-term process aimed at helping stroke survivors regain independence. In rehabilitation, the objectives are built on strength gain, continued improvement in function, and therefore, enhancement of the quality of life.
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy focuses on rebuilding strength and improving balance and mobility, while occupational therapy helps patients relearn daily activities like dressing, bathing, and cooking.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy is all about training people again for their daily life activities to take care of themselves.The therapists might suggest adaptive devices or home setups to make these tasks easy to perform.
Speech Therapy
Speech therapists direct patients with speech and communication defects, ranging from oration, and understanding, to even language impediments. Other dysphagia-which refers to swallowing conditions are also treated.
Cognitive and Emotional Restoration
Cognitive impairments are common after a stroke. Many patients suffer from problems concerning memory, problem-solving, and paying attention. In such a case, cognitive rehabilitation can restore lost mental capacities to the patient.
Emotional support is very important because many suffer from depression, anxiety, or frustration in the aftermath of the stroke. Counseling and support groups may help a victim in coping with various strategies and emotional outlets.
Rehabilitation varies based on the extent of the damage. Early intervention and continuous therapy will play a key role in the successful recovery.
Stroke outcomes and life expectancy depend on factors such as the severity of the stroke, the patient’s age, overall health, and access to treatment. Some remain with lifelong effects, while others recover remarkably well. Improvement in results mainly depends on good early intervention and continuous care. Rehabilitation brings back most of the survivors to an independent life and normal life.
Life expectancy after a mini-stroke (TIA) depends on managing risk factors like hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol, as it significantly increases the risk of a future stroke.With timely medical intervention and comprehensive rehabilitation, many stroke survivors can regain some or most of their lost functions. However, the risk of another stroke remains high within the first few months, making early treatment crucial for improving long-term outcomes.
Life after a stroke can be very challenging, but with the proper support and rehabilitation, one can overcome the obstacles and rebuild a life. Whether one is focused on regaining mobility, learning to do the things of daily routine once again, or coping with emotional struggles, the road to recovery is highly personal yet full of hope. By being informed, seeking early treatment and embracing rehabilitation, stroke survivors can look forward to a future full of possibilities.
Are you looking for effective stroke treatment in Bangalore? Walk Again Rehab offers a team of experienced therapists and cutting-edge facilities to support your recovery journey. Call us today to learn more.