Book an Appointment
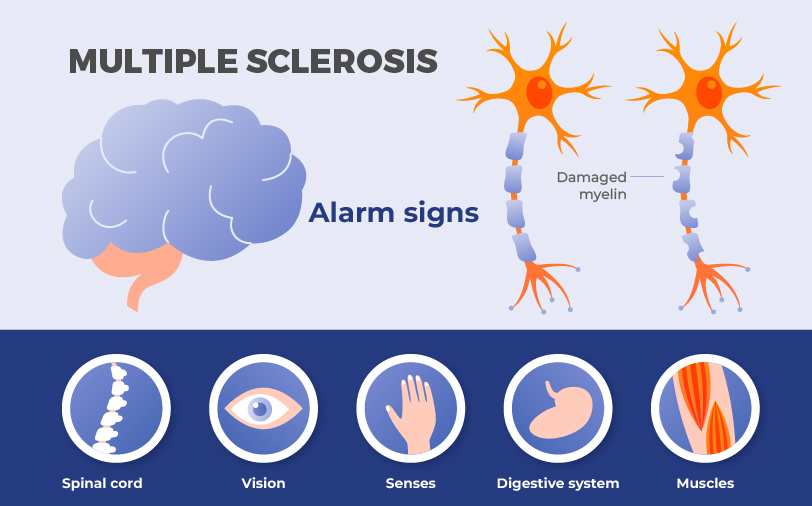
Call Us+91 9319488481Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a complex disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS). It presents with a wide range of symptoms that can vary greatly among individuals and impact many areas of daily life. While fatigue, muscle weakness, numbness, and dizziness are common symptoms of MS, their presence and severity can differ significantly from person to person and can change as the disease progresses. These symptoms can severely impact daily activities, mobility, and the ability to engage in social interactions. Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in managing MS, even though no cure currently exists. Multiple Sclerosis rehabilitation is not merely for treating the physical manifestations of the disease; it is a comprehensive, interdisciplinary process, that helps patients regain their quality of life.
To effectively manage the challenges of Multiple Sclerosis, various rehabilitation techniques are employed. Each method addresses specific aspects of the condition, aiming to improve overall well- being. The following sections explore advanced techniques in physical therapy, occupational therapy,
speech therapy, and neuropsychology, highlighting their roles in enhancing quality of life.
Physical therapy is an important part of MS rehabilitation, focusing on improving physical function and mobility through various targeted approaches.
Strengthening exercises Strengthening exercises are crucial for preventing muscle atrophy and improving overall strength. Regular, targeted exercises are essential and can be customized to focus on muscles most affected by MS, helping individuals maintain their strength and mobility.
Balance training
Gait problems are associated with MS, and the condition may also lead to balance issues that can result in falls. Physiotherapists help restore proprioception, or the positional sense of the body, which is vital for stability and correct movement. They engage patients in balance training exercises to improve stability and reduce fall risk.
Mobility aids
The Difficulty in moving from one place to another becomes more complex as the patient’s MS progresses. The utilization of mobility devices such as canes, walkers, or wheelchairs can promote independence and safety. Therapists recommend these devices to help clients choose the most suitable
ones and learn to use them correctly.
Hydrotherapy
Aerobic water exercise allows individual an opportunity to move freely and with minimal little pain. It is a well-known fact that Hydrotherapy helps to enhance muscle flexibility, decrease muscle tone, and induce relaxation.
In addition to physical therapy, occupational therapy plays an important role in helping individuals with MS manage daily tasks and adapt their environment to better support their needs.
Adaptive equipment
Occupational therapists focus on helping people with MS perform daily tasks as effectively as effective as possible. Special utensils for eating, dressing aids, and other modified kitchen tools can significantly reduce the effort required for these tasks.
Assistive technology
These include Assistive technologies to enhance communication, task organization, and interact with the computer interaction. These technologies can be particularly useful for individuals with MS who experience motor or cognitive deficits.
Home modifications
Installing grab bars, ramps, and stair lifts can make moving around the home easier and safer. An occupational therapist can evaluate the home and recommend modifications to prevent falls and improve navigation.
Addressing communication and cognitive challenges is another crucial aspect of MS rehabilitation, where speech therapy offers specialized support to improve verbal and cognitive skills.
Speech and language therapy
MS can impair speaking abilities. Speech therapists assist with pronunciation, tone, and intonation, and manage problems related to dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), which can be a significant complication in later stages of MS.
Cognitive rehabilitation
Symptoms such as fatigue, depression, irritability, memory impairment, and slow problem-solving are common in MS. Cognitive rehabilitation aims to improve these skills through various exercises, helping to prevent worsening and promoting greater independence.
Neuropsychology enhances cognitive functions by assessing mental processes affected by MS.
Cognitive assessments
Neuropsychologists conduct tests to assess cognitive and functional abilities, helping to identify both strengths and impairments. This evaluation is useful in designing cognitive rehabilitation programs tailored to individual needs.
Cognitive training
Cognitive training involves structured exercises designed to enhance specific forms of thinking, such as memory, attention, and problem-solving. These exercises aim to improve mental status and develop compensatory strategies.
Counseling
Living with MS can affect both physical and emotional well-being. Counseling services address the psychological aspects of the disease, assisting with anxiety, depression, and stress management.
The benefits of MS rehabilitation are profound and multifaceted.
Improved physical function: Cognitive-behavioral interventions of appropriate treatments and activities lead to marked gains in muscle strength, balance, and the ability to perform daily activities.
Enhanced quality of life: Rehabilitation helps reduce conditions such as fatigue, pain, and spasticity, which contribute to discomfort and decreased quality of life.
Improved cognitive function: Rehabilitation enables people with MS to perform cognitive tasks more effectively and with less support.
Increased independence: Rehabilitation approaches can enhance a patient’s ability to handle certain tasks independently, reducing dependency on caregivers and improving self-esteem.
Emotional support: Rehabilitation addresses the psychological aspects of MS, offering counseling or group support to help alleviate feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression.
Physical rehabilitation is crucial for managing multiple sclerosis, a chronic condition. Through physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, neuropsychology, and counseling, people with MS can significantly enhance their quality of life. Rehabilitation not only helps alleviate physical symptoms but also improves psychological and social well-being, enabling patients to lead more meaningful and independent lives.
Q: What does MS rehabilitation aim to achieve?
A: MS rehabilitation addresses mental, emotional, and cognitive difficulties to enhance quality of life. It supports overall well-being, improves independence, and helps manage symptoms.
Q: When should I begin my MS rehabilitation?
A: It is best to start MS rehabilitation as soon as possible after diagnosis to avoid complications and optimize benefits.
Q: Is MS rehabilitation effective?
A: Yes, MS rehabilitation has been shown to significantly improve an individual’s quality of life, cognitive function, emotional stability, and physical function.
Q: What kinds of exercises are suggested for people with MS?
A: Strengthening activities, balance training, and mobility exercises are frequently recommended for individuals with MS.
Q: Can speech therapy assist with difficulty swallowing?
A: Yes, speech therapists can help individuals with MS who have dysphagia by improving their swallowing abilities and reducing the risk of choking.
Q: Is there a cure for MS?
A: Currently, there is no cure for MS. However, rehabilitation can enhance quality of life and assist with symptom management.