Book an Appointment
Call Us+91 9319488481Cerebral palsy (CP) is a broad diagnostic term describing a group of non-progressive motor conditions caused by brain injury, which severely affects movement and coordination. While there is no cure for cerebral palsy, various treatments can help manage its symptoms. This blog provides an overview of cerebral palsy, including its causes, types, and symptoms, and focuses on different treatment methods. It also highlights treatment centers in Bangalore, which have evolved as preferred medical destinations in India.
Cerebral palsy is not a single disease but a group of disorders characterized by problems with movement, muscle tone, balance, and coordination. The condition results from injuries to the developing brain during pregnancy, childbirth, or shortly after birth. The brain damage impairs the control of muscle movements and coordination, leading to various signs and symptoms.
A key aspect of cerebral palsy is that the condition is non-progressive; the brain damage does not worsen over time. However, the physical and developmental challenges associated with CP can change as the individual grows.
The exact cause of cerebral palsy is often not well understood and usually arises from one or more factors causing brain injury at specific developmental stages. Known contributing factors include:
It is important to note that exposure to these risk factors does not necessarily mean a baby will develop cerebral palsy.
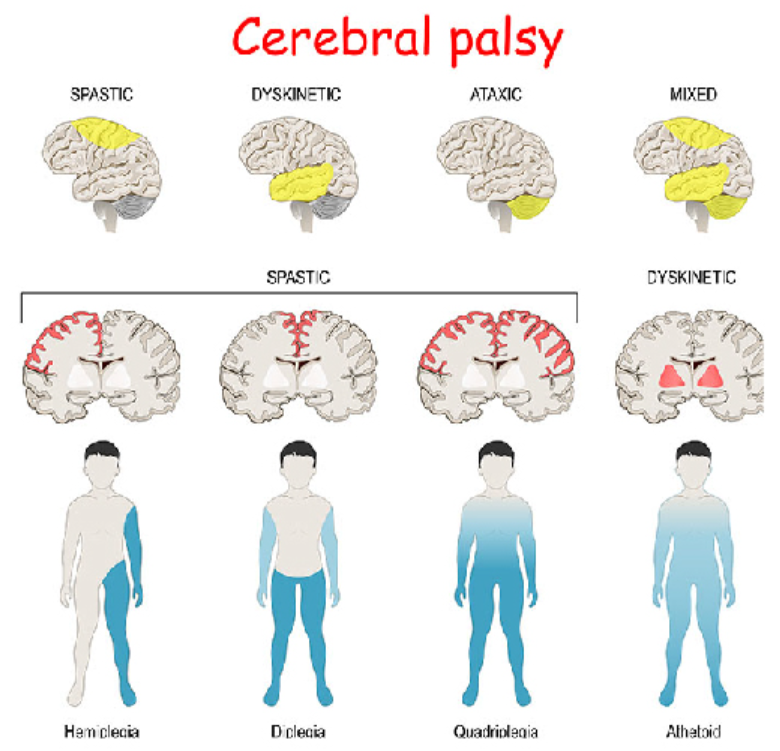
Cerebral palsy is classified into several types based on the nature of the movement disorder experienced by the individual:
Spastic Cerebral Palsy: This is the most common type, accounting for 70-80% of cases. It is characterized by involuntary muscle contractions leading to stiffness, twitching movements, and poor coordination. Depending on severity, spastic CP can affect one side of the body (hemiplegia), both sides of the legs and arms (diplegia), or all four limbs (quadriplegia).
Dyskinetic Cerebral Palsy: This type involves involuntary movements such as twisting, writhing, or jerking. These movements often increase with emotional stress or attempts at voluntary movement. Dyskinetic CP is associated with damage to the basal ganglia, a brain region responsible for movement coordination.
Ataxic Cerebral Palsy: This type impairs balance and coordination, leading to an unsteady gait, tremors, and difficulty with fine motor skills such as writing or buttoning a shirt. Ataxic CP is linked to damage in the cerebellum, the part of the brain that coordinates muscle movements.
Mixed Cerebral Palsy: Some individuals present with features of more than one type of CP, such as both spasticity and dyskinesia. This mixed form of the disorder is common.
The clinical manifestations of cerebral palsy vary based on the type and extent of the disorder. Common symptoms include:
Delayed Motor Skills: Delays in acquiring gross and fine motor skills, such as sitting, crawling, or walking, are often early indicators of CP.
Muscle Stiffness or Weakness: Muscles may be stiff (spastic) or weak (hypotonic), affecting motor skills and movement control.
Difficulty with Balance and Coordination: Individuals with ataxic CP may struggle with balance and coordination, impacting activities like walking or handling objects.
Problems with Speech and Swallowing: Motor speech issues, known as dysarthria, and swallowing difficulties (dysphagia) are common and can affect nutrition and overall well- being.
Learning Difficulties: Some children with CP may have learning disabilities or communication problems, although many have a typical IQ level.
Although cerebral palsy is a chronic condition, various treatments can significantly enhance quality of life. Treatment typically involves a combination of therapies and medical interventions tailored to the individual’s needs:
Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy is essential for the treatment of Cerebral palsy for improving muscle strength, flexibility, balance, and coordination.
Occupational Therapy: Focuses on enabling individuals to perform daily activities and addresses cognitive and sensory problems.
Speech Therapy: Helpful for addressing speech and language impairments, as well as swallowing difficulties.
Assistive Devices: Mobility aids, communication devices, orthotic appliances, and braces can support movement and prevent contractures.
Medications: Used to manage symptoms such as muscle spasticity, pain, and seizures.
Surgery: Surgery may be required to correct physical abnormalities or alleviate severe muscle tone. Common procedures include bone and joint surgeries and selective dorsal rhizotomy (SDR), which involves severing some nerve root fibers to reduce spasticity in the legs.
Bangalore, known as the ‘Silicon Valley of India,’ is also recognized as a leading destination for medical tourism. The city boasts some of the leading cerebral palsy treatments and several premier hospitals and specialized centers for neurology and neuro-rehabilitation, particularly for children. These centers are well-equipped with advanced medical technologies and offer comprehensive treatment services.
While cerebral palsy is a serious condition, proper medical and rehabilitation services can greatly improve the quality of life for individuals affected by it. Parents and caregivers should seek professional guidance and develop tailored treatment plans to support the child’s needs. With appropriate intervention and support, individuals with cerebral palsy can lead fulfilling and happy lives.